Free electron laser atomic, molecular, and optical physics program package
(FELLA)
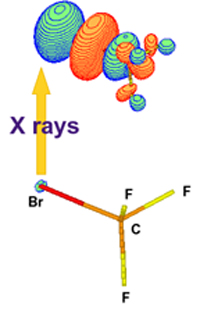 Electron from a
Br 1s orbital excited to the σ* orbital of CF3Br by x-ray
absorption.
For more information, see "An x-ray probe of laser-aligned molecules,”
Applied Physics Letters 92, 094106 (2008) and "Strong-field
control of x-ray absorption," J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 88, 012052
(2007).
Electron from a
Br 1s orbital excited to the σ* orbital of CF3Br by x-ray
absorption.
For more information, see "An x-ray probe of laser-aligned molecules,”
Applied Physics Letters 92, 094106 (2008) and "Strong-field
control of x-ray absorption," J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 88, 012052
(2007).
Manifesto
FELLA (Free Electron Laser Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
Program Package) is a software package developed by Argonne researchers
to explore the ultrafast and the ultrasmall.
The authors have written FELLA for highly specialized basic research in
atomic, molecular, and optical physics.
The atomic physics programs treat the atomic electronic structure in
Hartree-Fock-Slater approximation and the interaction of electrons with
light of up to two colors.
The molecular physics programs treat the X-ray absorption by laser-aligned
molecules.
An optical physics code describes the propagation of a laser and X-rays
through a gaseous medium.
There are additional miscellaneous small helper programs.
FELLA has been inspired by the upcoming X-ray free electron lasers (FEL)
to study atoms and molecules in their light in combination with intense
optical lasers.
However, FELLA is more general and has been used so far to study atoms
and molecules in the light of third-generation synchrotrons such as
Argonne’s Advanced Photon Source.
The software, written in FORTRAN95, currently is in Version 1.3.0.
The software can be run on a PC with the Linux operating system and
the free g95 FORTRAN95 compiler.
There is no manual at this time.
The source code is well documented with comments.
An example input is provided with a description of the input parameters.
The meaning of the values selected is published.
The code is relatively user-friendly and running times can vary from
15 minutes to several weeks depending upon the input parameters, with
most cases being run in a few days.
This software is of value to universities studying laser-matter
interactions as well as to national laboratories that can generate
X-rays for experimental use.
The upcoming X-ray FEL facilities such as those at Stanford
(LINAC Coherent Light Source (LCLS)), Hamburg, Germany
(European X-Ray Laser Project (XFEL), and Harima Science Garden City,
Hyogo, Japan (SPring-8 Compact SASE Source (SCSS) could potentially
benefit from FELLA.
Citation
In publications, please use the following citation:
Christian Buth, "fella (Free Electron
Laser Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics Program Package)", Version 1.4.0,
Theoretische Chemie, Physikalisch-Chemisches Institut,
Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg,
Im Neuenheimer Feld 229, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany, with
contributions by Mark Baertschy, Kevin Christ, Chris H. Greene,
Hans-Dieter Meyer, Robin Santra, and Thomas Sommerfeld (2017).
Download
Copyright Notice
FELLA
Copyright © 2008 UChicago Argonne, LLC
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
met:
- Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
- Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
- The end-user documentation included with the redistribution, if
any, must include the following acknowledgment: "This product includes
software developed by the UChicago Argonne, LLC as Operator of Argonne
National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357 with the
Department of Energy (DOE)."
Alternately, this acknowledgment may appear in the software itself,
if and wherever such third-party acknowledgments normally appear.
- WARRANTY DISCLAIMER. THE SOFTWARE IS SUPPLIED "AS IS" WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND. THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER, THE UNITED STATES, THE
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY, AND THEIR EMPLOYEES: (1) DISCLAIM
ANY WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
TITLE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT, (2) DO NOT ASSUME ANY LEGAL LIABILITY OR
RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE ACCURACY, COMPLETENESS, OR USEFULNESS OF THE
SOFTWARE, (3) DO NOT REPRESENT THAT USE OF THE SOFTWARE WOULD NOT
INFRINGE PRIVATELY OWNED RIGHTS, (4) DO NOT WARRANT THAT THE SOFTWARE
WILL FUNCTION UNINTERRUPTED, THAT IT IS ERROR-FREE OR THAT ANY ERRORS
WILL BE CORRECTED.
- LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. IN NO EVENT WILL THE COPYRIGHT
HOLDER, THE UNITED STATES, THE UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY,
OR THEIR EMPLOYEES: BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
CONSEQUENTIAL, SPECIAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND OR NATURE,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF PROFITS OR LOSS OF DATA, FOR
ANY REASON WHATSOEVER, WHETHER SUCH LIABILITY IS ASSERTED ON THE
BASIS OF CONTRACT, TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR STRICT LIABILITY),
OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF ANY OF SAID PARTIES HAS BEEN WARNED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH LOSS OR DAMAGES.
- Portions of the Software resulted from work developed under a
U.S. Government contract and are subject to the following license:
the Government is granted for itself and others acting on its behalf
a paid-up, nonexclusive, irrevocable worldwide license in this computer
software to reproduce, prepare derivative works, and perform publicly
and display publicly.
FELLA Publications
M. B. Gaarde, C. Buth, J. L. Tate, K. J. Schafer, Transient
absorption and reshaping of ultrafast xuv
light by laser-dressed helium, Phys. Rev. A 83, 13419 (2011).
C. Buth, R. Santra, and L. Young, "Refraction and absorption of X-rays
by laser-dressed atoms," Revista Mexicana de Fisica (accepted for
publication)
L. Young, C. Buth, R. W. Dunford, P. J. Ho, E. P. Kanter, B. Krässig,
E. R. Peterson, N. Rohringer, R. Santra, and S. H. Southworth, "Using
strong electromagnetic fields to control X-ray processes," Revista
Mexicana de Fisica (accepted for publication)
C. Buth and R. Santra, "X-ray refractive index of laser-dressed atoms,"
Physical Review A 78, 043409 (2008).
C. Buth and R. Santra, "Rotational molecular dynamics of
laser-manipulated bromotrifluoromethane studies by X-ray absorption,"
The Journal of Chemical Physics 129, 134312 (2008).
E. R. Peterson, C. Buth, D. A. Arms, R. W. Dunford, E. P. Kanter,
B. Krässig, E. C. Landahl, S. T. Pratt, R. Santra, S. H. Southworth,
and L. Young, “An x-ray probe of laser-aligned molecules,” Applied
Physics Letters 92, 094106 (2008).
C. Buth and R. Santra, “Theory of X-ray absorption by laser-aligned
symmetric-top molecules,” Physical Review A 77, 013413 (2008).
C. Buth, R. Santra, and L. Young, “Electromagnetically induced
transparency for X-rays,” Physical Review Letters 98, 253001 (2007).
R. Santra, C. Buth, E. R. Peterson, R. W. Dunford, E. P. Kanter,
B. Krässig, S. H. Southworth, and L. Young, "Strong-field control
of x-ray absorption," J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 88, 012052 (2007).
Z-H. Loh, M. Khalil, R. E. Correa, R. Santra, C. Buth, and
S. R. Leone, "Quantum state-resolved probing of strong-field-ionized
xenon atoms using femtosecond high-order harmonic transient absorption
spectroscopy," Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 143601 (2007).
C. Buth and R. Santra, "Theory of X-ray absorption by laser-dressed
atoms," Phys. Rev. A 75, 033412 (2007).
Funding
Funding was provided by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of
Science, Basic Energy Sciences, Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and
Biosciences, and by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Bonn, Germany.
© 2017  Dr. Christian Buth
[homepage @ christianbuth.name]
Dr. Christian Buth
[homepage @ christianbuth.name]
URL of this page: http://www.christianbuth.name/fella.html.
 Electron from a
Br 1s orbital excited to the σ* orbital of CF3Br by x-ray
absorption.
For more information, see "An x-ray probe of laser-aligned molecules,”
Applied Physics Letters 92, 094106 (2008) and "Strong-field
control of x-ray absorption," J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 88, 012052
(2007).
Electron from a
Br 1s orbital excited to the σ* orbital of CF3Br by x-ray
absorption.
For more information, see "An x-ray probe of laser-aligned molecules,”
Applied Physics Letters 92, 094106 (2008) and "Strong-field
control of x-ray absorption," J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 88, 012052
(2007).